Adding Awesomplete to Vue Components
 IBM Model M SSK by njbair, used under CC BY-SA 2.0 / Cropped from original
IBM Model M SSK by njbair, used under CC BY-SA 2.0 / Cropped from original
Awesomplete is an “Ultra lightweight, customizable, simple autocomplete widget with zero dependencies, built with modern standards for modern browsers.”
Awesomplete caught my attention when I was looking for a lightweight autocomplete implementation to add to an existing, heavily styled form in a Vue.js single-file component. There are no fewer than 10 options on the Awesome Vue.js list of autocomplete libraries, but many of them brought their own dependencies or custom styling and I was looking for something simpler to add autocomplete features to my form.
I have created a live JSFiddle demo showing an implementation of Awesomplete in a Vue.js app, but the remainder of this post contains more details about adding Awesomplete to a single-file component in a larger Vue application.
Here is a screenshot and sample code for a simplified version of the Vue single-file component that I was working with:
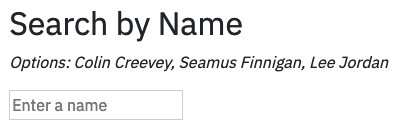
<template>
<div>
<h2>Search by Name</h2>
<p>
<em>
Options: {{ names.join(', ') }}
</em>
</p>
<form>
<input
id="name-input"
placeholder="Enter a name"
type="text"
>
</form>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data () {
return {
names: [
'Colin Creevey',
'Seamus Finnigan',
'Lee Jordan'
]
}
}
}
</script>In my actual application I was populating the data object with API data via vue-apollo, but I’ve hard-coded the array of strings here for simplicity.
Adding autocomplete to my form with Awesomplete was as easy as adding the package to my project with yarn awesomplete and then updating the Vue component to load the library and attach it to my form:
<template>
...
</template>
<script>
import Awesomplete from 'awesomplete'
export default {
data () {
return {
names: [
'Colin Creevey',
'Seamus Finnigan',
'Lee Jordan'
]
}
},
mounted () {
let input = document.getElementById('name-input')
new Awesomplete(input, { minChars: 3, list: this.names })
input.addEventListener('awesomplete-select', (e) => {
alert(`selected ${e.text.value}`)
})
}
}
</script>All of the Awesomplete work is taking place in the component’s mounted() function, where the form input is stored in a variable, passed to a new Awesomplete instance along with an options object, and then a listener function is added to take some action when the user has selected an autocomplete value. That action would typically be a form submission, but I am just using an alert for the purposes of this demo.
Awesomplete has many options for customization and is well-documented in general. I encourage anyone looking to add autocomplete features to their projects to give it a try; I was impressed by how easily I was able to use it to add autocomplete features that integrated well with my project.

Comments